Smart Home Protocols Explained: Wi-Fi vs Bluetooth vs Zigbee vs Z-Wave Vs Thread and Matter
Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Thread, Z-Wave, and Matter are ways for devices in smart homes to communicate with each other. They’re often described as wireless protocols, communication standards, and wireless technologies. How do they work? What sets them apart from one another? Is there a superior protocol among them? In this blog post, we will address these inquiries and provide a comprehensive understanding of how you can leverage them to your benefit.

What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi, short for Wireless Fidelity, is a wireless communication technology that allows devices to connect to the internet and communicate with each other wirelessly. It is based on the IEEE 802.11 standards and operates in the unlicensed radio frequency bands, typically 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz.
Wi-Fi enables devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, smart TVs, and smart home devices to establish a wireless connection to a local area network (LAN) or the internet. It provides high-speed data transmission and allows users to access online services, browse the web, stream media, and transfer files without the need for physical cables.

Wi-Fi Vs Zigbee Vs Z-Wave Vs Bluetooth - What’s the Difference
Choose Wi-Fi for Wide Compatibility, High Bandwidth, and Direct Connection to the Internet
Wi-Fi is everywhere. Almost every home has it, and each Wi-Fi smart device has its own built-in ability to communicate over Wi-Fi. The transmission bandwidth of WiFi is the largest, and it has reached hundreds of Mbps. As long as you have a wireless router, you can access it to transmit high-definition video, lossless audio, and high-precision pictures. Wi-Fi is connected to the internet so it will be possible to control and monitor a range of smart devices in your home from anywhere in the world via your smartphone, tablet, or laptop.
However, Wi-Fi is power-hungry. Wi-Fi has strong transmission capability and wall penetration ability. It has the most powerful performance, but the power consumption of WiFi is so high that it is not suitable for battery-powered devices and is more suitable for plug-in devices.

Wi-Fi in Smart Home
What is Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks. Its frequency is 2.4 GHz, transmission range is 50~150 meters. Bluetooth 5 offers four different data rates to accommodate a variety of transmission ranges: 2Mbps, 1Mbps, 500kbps, and 125kbps. The technical specification of Bluetooth includes three classes of ERP 1-3 transmission power, and ranges of 100, 10, and 1 meter in open space. The second (10m) class, which enables you to connect devices in various rooms and even on different floors, is the most popular.
In Bluetooth technology, data is transmitted as packets to one of 79 channels with a bandwidth of 1 Mhz (in the case of the oldest Bluetooth 1.0 standard), ensuring a maximum transfer speed of 721 kbit/s. A maximum data transfer rate of up to 3 Mb/s is ensured by the 40 channels and 2 Mhz bandwidth of the most recent Bluetooth 4.0 standard (BLE).
What Role Does Bluetooth Low Energy Play in a Smart Home?
Smart home devices use Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), which consumes less energy than standard Bluetooth, because devices remain in a low-power state for most of the time.
The advantage of Bluetooth Low Energy for smart device operation is the ease of adoption and broad compatibility. For example, if you install the Philips Hue Bluetooth app on your phone you can control up to 10 Hue smart LED lights, without needing to buy a smart display or a smart hub like Hue Bridge).

Feature Comparison
But Bluetooth Low Energy has disadvantages. Firstly, it offers significantly less bandwidth than Wi-Fi, which is why smart cameras and video doorbells tend to use Wi-Fi - video data transmits much better with the bigger bandwidth.
Bluetooth technology is also quite slow to respond to commands. When compared to the alternative technology you can now choose to control your smart devices, like Zigbee, Z-Wave, Thread and Matter, there’s a noticeable delay in the response of smart devices using Bluetooth.
What is Zigbee?
Zigbee is a wireless networking standard, and its specifications are maintained and updated by the non-profit organization Zigbee Alliance, which was established in 2002. There are more than 400 tech firms that support that standard including behemoths like Apple, Amazon, and Google, alongside names such as Belkin, Huawei, Ikea, Intel, Qualcomm, and Signify, as well as many others.
The Zigbee standard can broadcast data across distances of approximately 82 to 109 yards / 75 to 100 meters indoors, or around 328 yards / 300 meters in the open air, meaning it can easily offer strong, stable coverage in large homes.

Zigbee Alliance
How Does Zigbee Work in a Smart Home?
Zigbee sends instructions between smart home devices, from a smart speaker to a light bulb, for example, or from a switch to a bulb – without first going via a central control hub, like a Wi-Fi router. This signal can also be sent and understood by the recipient device. no matter which manufacturer made it. So long as they all support Zigbee, they speak the same language.
Zigbee operates as a mesh network, which means instructions can be sent between devices attached to the same Zigbee network. In theory, each device acts as a node, receiving and transmitting data to every other device, helping the instructions data spread further and the smart home network can cover a large area.

Zigbee Mesh Network
The mesh structure of a Zigbee network also means there’s no one point of failure in the network. For example, if you have a home full of Zigbee-compatible smart light bulbs, you may want them all to be illuminated at the same time. If one isn’t working properly, the mesh ensures the command will still be passed to every other bulb in the network.
Zigbee may not be as commonplace as Wi-Fi, but it is featured in a surprising number of products; the Zigbee Alliance has over 400 members from 35 countries. The Alliance also says there are over 2,500 Zigbee-certified products and more than 300 million have been produced to date.
What is Z-wave?
Z-Wave is a wireless communications protocol that sends data between connected devices. Similar to Zigbee, Z-Wave uses mesh networking technology that enables devices to communicate with each other and form an interconnected network. Z-Wave operates on a lower radio frequency than Wi-Fi and Zigbee, which reduces the likelihood of interference from other wireless devices and directly improves device reliability, thanks to the lack of competition on the same frequency. A Z-Wave network consists of a ‘controller’ and one or more ‘slaves’.
The Z-Wave controller (often referred to as a Z-Wave hub) is used for:
- starting and establishing the network
- adding or removing devices from the Z-Wave network
- bridges the Z-Wave network to your home Wi-Fi network.

Z-wave Mesh Network
How Does Z-wave Help Connect Smart Homes?
A Z-Wave slave is a smart home device, like a smart lock or sensor. Similar to Zigbee, mains-powered Z-Wave devices act as repeaters of the mesh network, so as you add more Z-Wave smart plugs or sensors, the reliability and range of the mesh network increases.
One of the reasons Z-Wave is popular is due to its interoperability - the ability to exchange and make use of information - across different brands. This means any smart device with the Z-Wave logo will work seamlessly with another Z-Wave-enabled device, whatever company made it.

Wi-Fi Vs Zigbee Vs Z-Wave - What’s the Difference?
Zigbee vs Wi-Fi and Z-Wave have different features that provide their own pros and cons. These are:
Availability
Wi-Fi is ubiquitous as it operates through a router on the universally-accepted 2.4 GHz. Similarly, Zigbee also operates on the universally accepted 2.4 GHz band. It facilitates the manufacturing process as the same chip can be used to distribute products around the world.
On the other hand, Z-Wave products can only communicate in a certain range of government frequencies. In the USA, the Z-Wave products use 908 MHz while in Europe, 868 MHz is used. Numerous other frequencies are available in different parts of the world. Most manufacturers produce only limited Z-Wave products for the US and Europe.
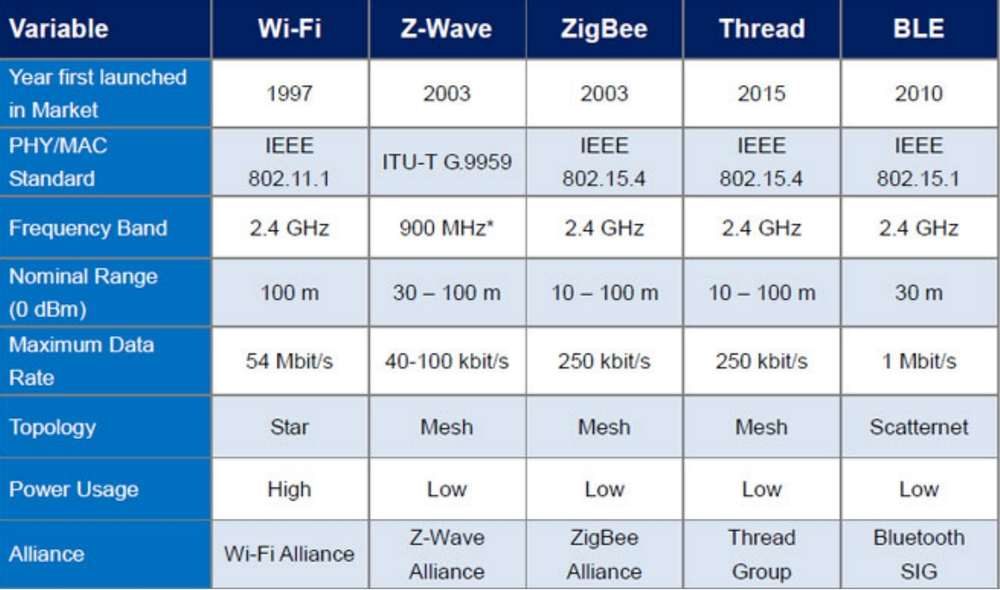
Interoperability
Most of the Wi-Fi is interoperable, especially the ones that use the same networking protocols. Some manufacturers provide company-specific integrations. Major companies like Amazon and Google provide their own Wi-Fi integration like smart speakers and other smart home products.
All of the Z-Wave products are interoperable because a single organization, Sigma Design, certifies them. The entire certification process ensures that all of the products are compatible with the whole Z-Wave ecosystem. The large-scale interoperability has helped the Z-Wave in quickly increasing its industry adoption. According to an estimate, there are more than 3,000 Z-Wave-certified products available on the market.
On the contrary, Zigbee has suffered a lot due to its failure to implement interoperability standards. Zigbee had to face a lot of fraudulent activities, especially in its starting years. In 2007, the Zigbee Pro standard was introduced to increase interoperability and prevent fraud. Zigbee 3.0 products have very impressive interoperability now.
Computability
Out of Zigbee and Z-Wave, Wi-Fi is the only smart home technology that is supported by all three major platforms: Amazon, Google, and Apple. You can also add a multi-tech hub that will offer more flexible and efficient features. It is very easy to integrate Wi-Fi products with most companies because it is a very well-known technology.
An extensive range of multi-tech hubs like Vera and SmartThings support Zigbee. Moreover, many open-source programs also support Zigbee devices. However, Zigbee's computability is certainly much less than Wi-Fi devices. On the other hand, almost every multi-tech hub and home software program supports Z-Wave. However, Amazon or Google smart speakers do not support Z-Wave.
What is Thread?
Thread is a wireless protocol specifically built for IoT devices. It’s designed to make them work faster, have fewer points of failure, use less power, and communicate with each other more seamlessly.
A low-power, low-bandwidth mesh networking protocol that uses the 802.15.4 radio technology, Thread is similar to existing smart home protocols Zigbee and Z-Wave. But unlike them, it doesn’t need a central hub or bridge. Instead, Thread devices can talk directly to each other. By cutting out the middle man, Thread can be faster, especially over large networks.
Also, unlike the other low-powered smart home protocols, Thread is an internet protocol (IP)-based, meaning it can directly connect to any other IP-based device, such as smartphones, tablets, computers, and Wi-Fi routers.

Scalable low-power mesh
How Does Thread Work in a Smart Home?
Thread was designed from the ground up to be an IoT low-power protocol that supports low latency. That’s its purpose. A lot of the other technologies used in the smart home were designed to optimize other applications. For example, Bluetooth was originally designed as a wire replacement. Thread was designed for devices that just want to sleep for a long time, wake up, send a single packet, and then go back to sleep and preserve battery for as long as possible.
Thread’s direct communication capability, combined with its ability to handle scale (over 250 devices), means lower latency. Benchmarking tests run by Silicon Labs show Thread thrashing Zigbee and Bluetooth in latency tests, especially in large networks with many devices. A Thread mesh can work as a routed mesh, which means the devices are proactively looking for the best route to every other device in the network. This efficiency translates directly into reduced power consumption as well as reduced latency. As a mesh network, Thread is self-healing; if a router (see sidebar) drops offline, another one can pick up the slack so your network doesn’t go down.

What is Matter?
Matter is a smart home standard created by Project Connected Home Over IP (Project Chip) in 2019. It is a new, open-source standard that uses a wireless technology based on Internet Protocol (IP), which Wi-Fi routers use to assign an IP address to each connected device. It's now maintained by the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA), formerly the Zigbee Alliance. The standard is royalty-free and encourages interoperability between devices and platforms. Matter is officially launched in November 2022.
Matter is an application layer protocol that runs on different physical layer protocols, including Thread, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet. The goal of Matter is to provide a unified standard that enables interoperability and compatibility among smart home devices. It defines the communication and interaction methods between devices, allowing seamless collaboration between different brands and types of smart home devices.
What Problems Does Matter Solve?
- Set up a universal standard: IoT devices have been around for years, yet they were separated into their unique categories. There wasn't a universal standard to bring them together, which was one of the biggest hurdles we've had to overcome. Between Zigbee, Z-Wave, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi, the wireless connectivity space for smart home and IoT devices became too crowded for its own good.
- Constant internet connection: IoT devices have previously relied exclusively on the cloud for everything, making them useless when losing the internet connection. Matter allows devices to work offline without requiring continuous access to the cloud and various cloud services. Less reliance on the cloud also means increased security for the devices — essential for sensitive hardware like smart locks and security cameras.
What are the Problems with Matter?
Nothing is perfect, and while it's a lot better than its predecessors, Matter has a few drawbacks. Introducing a new standard relies on widespread adoption. The number of Matter-enabled smart devices is increasing. Eve, Meross Nanoleaf, Hue, Comcast, and Toya are some of the brands updating or creating new Matter-enabled solutions. Look for the Matter smart home badge when you purchase new devices or accessories. If you're wondering if your existing devices will get the Matter update, refer to the manufacturers' websites.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Thread, Z-Wave, and Matter are all prominent communication protocols used in smart homes. Each protocol has its unique characteristics and advantages, catering to different device requirements and use cases.
As more and more companies join the Thread and Matter camps and incorporate them into their product ecosystems, these two technologies will gradually become the mainstream standards for smart home devices. However, it is important to note that there are still many smart home devices in the market that use other communication protocols. Therefore, in the foreseeable future, we may see a coexistence of various communication technologies, with their reasonable applications in specific device types or use cases. But the overall trend is that Thread and Matter will play a significant role in the smart home industry and gradually become the preferred choice.
Learn more about A Comprehensive List of Top Wireless Technologies




